This paper outlines a novel architecture blueprint that use large language models (LLMs) to enhance ad targeting effectiveness through personalized messaging.
In 2017, Netflix demonstrated the impact of personalized promotional messaging by adapting artwork based on user preferences and viewing history. The company’s content experts generated multiple images for every title and change them regularly to lure audiences based on their previous viewing history. The approach utilized a sophisticated “online reinforcement learning” strategy, optimizing the balance between exploiting known user preferences and exploring new data for improved recommendations. This dynamic methodology was essential in minimizing the cumulative “regret” (defined as the difference between the expected “payoff” (e.g. engagement) of the algorithm and the payoff of a single fixed strategy for selecting artworks) and enhancing viewer satisfaction over time.
Despite its efficiency, this approach epitomized a few key principles under the legacy Personalization 1.0 paradigm, namely the need to choose between a finite set of creatives (while being limited by multimodal content creation’s cost and complexity), the reliance on high-quality (and therefore expensive) human preference labels to optimize algorithmic tuning, and the use of shallow context information (e.g. transient signals like search history) as proxies for viewers’ interests. Today’s advancements in Generative AI necessitate a complete re evaluation of the algorithmic / architectural trade-off and its relevance.
This paper outlines...
Exclusive Content
This article is available with a Technical Paper Pass
Opportunities for emerging 5G and wifi 6E technology in modern wireless production
This paper examines the changing regulatory framework and the complex technical choices now available to broadcasters for modern wireless IP production.
Leveraging AI to reduce technical expertise in media production and optimise workflows
Tech Papers 2025: This paper presents a series of PoCs that leverage AI to streamline broadcasting gallery operations, facilitate remote collaboration and enhance media production workflows.
Automatic quality control of broadcast audio
Tech Papers 2025: This paper describes work undertaken as part of the AQUA project funded by InnovateUK to address shortfalls in automated audio QC processes with an automated software solution for both production and distribution of audio content on premises or in the cloud.
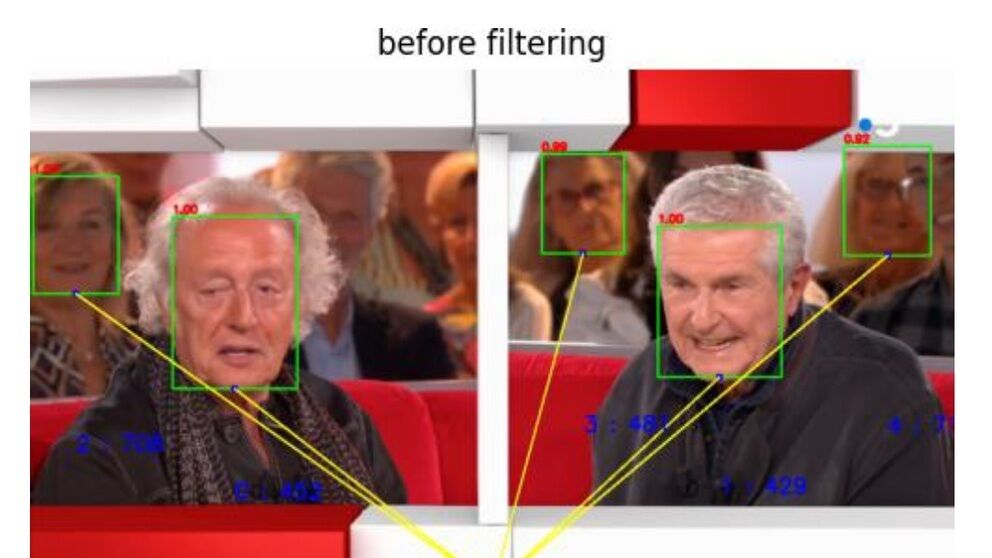
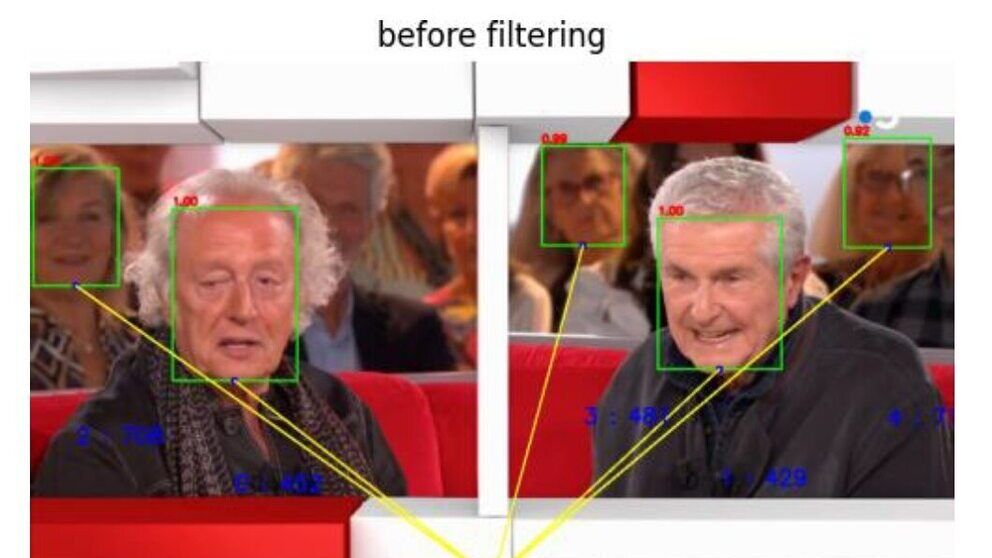
Demonstration of AI-based fancam production for the Kohaku Uta Gassen using 8K cameras and VVERTIGO post-production pipeline
Tech Papers 2025: This paper details a successful demonstration of an AI-based fancam production pipeline that uses 8K cameras and the VVERTIGO post-production system to automatically generate personalized video content for the Kohaku Uta Gassen.
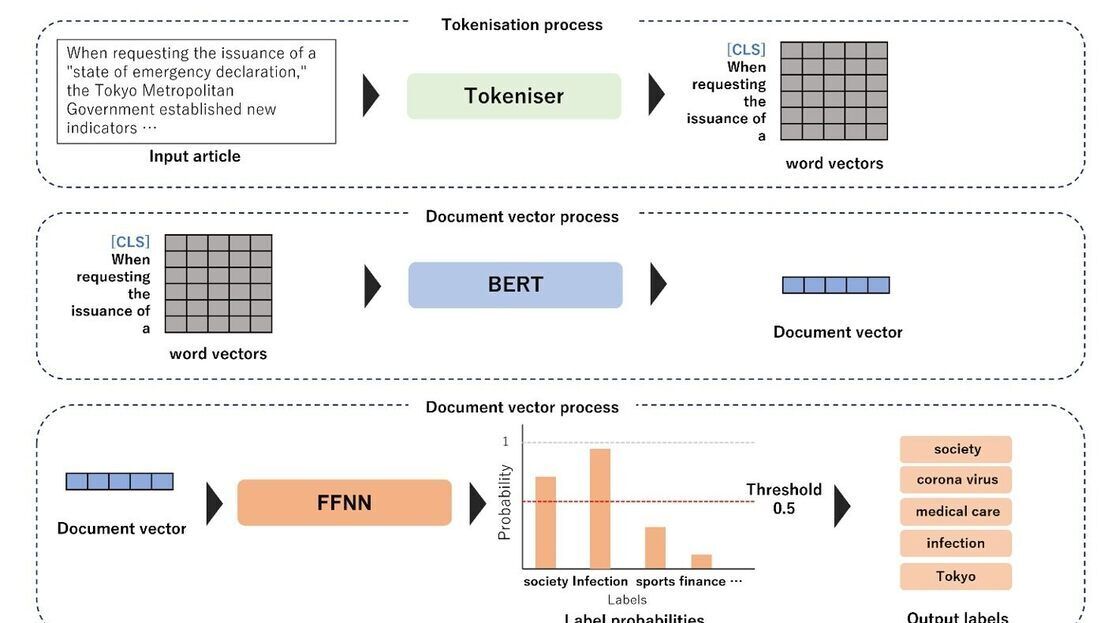
EBU Neo - a sophisticated multilingual chatbot for a trusted news ecosystem exploration
Tech Papers 2025: The paper introduces NEO, a sophisticated multilingual chatbot designed to support a trusted news ecosystem.